In the world of trading, knowing where the “true average price” of an asset lies during the trading day is crucial. That’s where VWAP, or Volume Weighted Average Price, comes in. VWAP is more than just another line on your chart—it’s a powerful indicator that combines price and volume to give traders insight into market value and potential direction. Whether you’re a day trader, swing trader, or institutional investor, understanding VWAP can give you a significant edge.
What is VWAP?
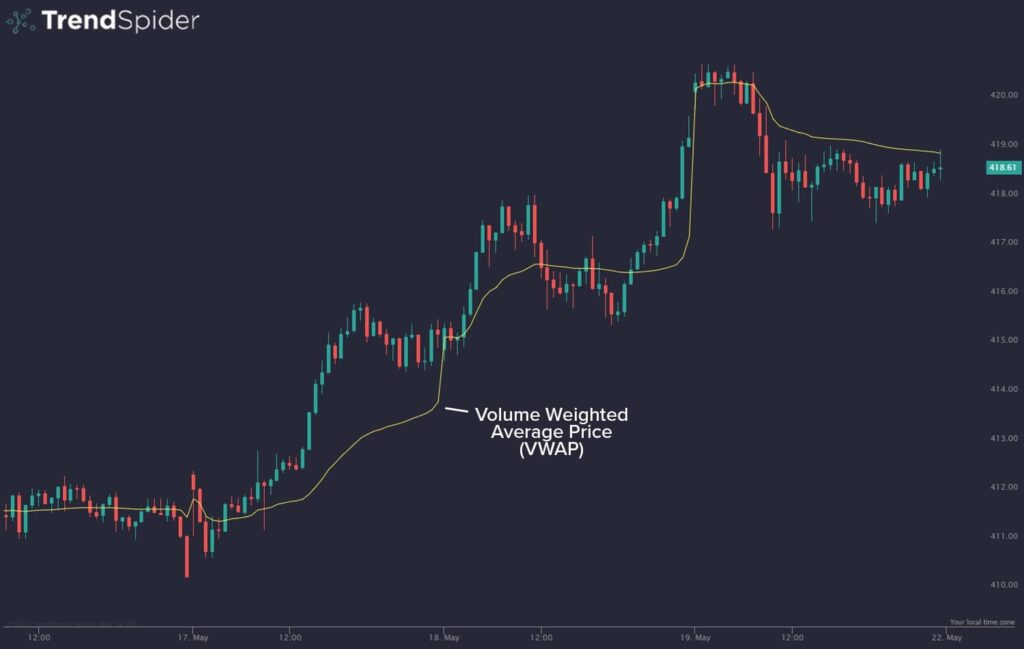
VWAP stands for Volume Weighted Average Price. It is a trading benchmark that reflects the average price a security has traded at throughout the day, based on both volume and price. Unlike simple moving averages (which only consider price), VWAP adds an essential layer—volume—into the equation. This makes it a more realistic representation of market consensus.
The VWAP is calculated using this formula:
VWAP = (Cumulative Price × Volume) ÷ Cumulative Volume
This means each trade contributes to the VWAP based on how much volume it carries. Larger trades have more influence, giving a better representation of where the majority of market participants are transacting.
Why is VWAP Important?
VWAP is especially popular among institutional traders and hedge funds because it helps measure trading efficiency. Institutions use VWAP to ensure they are getting fair prices for large trades without moving the market too much.
But even if you’re not moving millions of dollars around, VWAP has multiple uses:
- Trend confirmation
- Dynamic support and resistance
- Entry and exit signals
- Measuring institutional buying or selling pressure
Let’s look at how this indicator can help you make better decisions.
How to Use VWAP in Trading
1. Trend Confirmation Tool
VWAP can help confirm the trend of the day. When the price is above VWAP, it indicates that buyers are in control and the market is likely bullish. When the price is below VWAP, it signals that sellers are dominant and the market is bearish.
In day trading, many traders look for confirmation from VWAP before entering a position. For example, in an uptrend, you may want to buy on pullbacks to VWAP. In a downtrend, you might sell or short on rallies to VWAP.
2. Support and Resistance
VWAP often acts as a dynamic support or resistance level. If the price is trending above VWAP and starts pulling back, VWAP can act as a support level where price may bounce. Conversely, in a downtrend, VWAP often serves as a resistance line.
This is particularly useful for intraday trading, where levels constantly change and need real-time adjustment.
3. Institutional Benchmarking
Institutions often aim to buy below VWAP and sell above it to achieve better trade execution. If they buy below VWAP, they can report that they executed the trade at a better-than-average market price. This institutional behavior can influence price action, especially near the VWAP line.
4. Entry and Exit Signals
You can develop a strategy based on VWAP crossovers. For example:
- Long Signal: Price crosses above VWAP + confirms volume spike
- Short Signal: Price crosses below VWAP + bearish candle formation
To filter out false signals, many traders combine VWAP with other indicators like RSI, MACD, or candlestick patterns.
VWAP vs Moving Averages
Many traders confuse VWAP with moving averages like the 20 EMA or 50 SMA. While they can appear similar on a chart, they serve different purposes.
- VWAP resets daily and is intraday-focused.
- Moving averages continue over multiple days and are better for swing or position trades.
The volume component makes VWAP more sensitive to significant trades, giving a more accurate representation of real price action during the day.
Types of VWAP
There are several variations of VWAP that traders use, depending on their needs:
1. Standard VWAP
Resets daily. Most common type used by intraday traders.
2. Anchored VWAP
This version allows you to anchor the VWAP to a specific time, candle, or event (e.g., earnings, breakout point). It’s useful for swing traders or for tracking sentiment after major market events.
3. Rolling VWAP
Used for longer-term analysis. It calculates VWAP over a rolling window (e.g., 5 days, 20 days) instead of resetting daily.
Each of these can offer different insights depending on your strategy and timeframe.
VWAP Trading Strategies
Let’s explore two common VWAP-based strategies that you can test and incorporate.
Strategy 1: VWAP Pullback in Uptrend
- Setup: Identify a stock trading above VWAP after a strong morning rally.
- Trigger: Wait for a pullback to VWAP with a bullish candlestick pattern (e.g., hammer, engulfing).
- Entry: Buy near VWAP with tight stop below it.
- Target: Previous high or a set risk/reward ratio.
This is a high-probability setup used by many day traders to catch the continuation of a trend after a healthy pullback.
Strategy 2: VWAP Reversal
- Setup: A stock has been trending below VWAP for most of the day but shows signs of reversal (bullish divergence on RSI, decreasing volume on lows).
- Trigger: Price breaks above VWAP with strong volume.
- Entry: Buy the breakout or wait for a VWAP retest.
- Target: Next resistance or fib level.
This strategy aims to catch reversals when the market sentiment shifts and price crosses above VWAP.
Limitations of VWAP
Despite its usefulness, VWAP is not perfect:
- Only intraday: Standard VWAP resets daily, making it less effective for multi-day analysis unless you use Anchored VWAP.
- Lagging nature: Since it’s an average, VWAP may react slowly to sudden price changes.
- False signals: Especially during low-volume periods or choppy markets, price can cross VWAP multiple times without real direction.
To avoid these pitfalls, VWAP should be used in conjunction with other tools and proper risk management.
Best Timeframes and Markets
VWAP works best in liquid markets like:
- Stocks
- ETFs
- Futures
- Forex (on high-volume pairs)
It’s most effective on 1-minute to 15-minute charts, especially during the first 2 hours of the trading day when volume is highest.
Final Thoughts
VWAP is a versatile and powerful indicator that provides insight into the average price level weighted by volume. It offers clarity on where big players are positioning themselves, and acts as a solid reference point for entries, exits, and trend confirmation.
Whether you’re a scalper looking for quick profits or an intraday trader wanting to avoid buying the top or selling the bottom, incorporating VWAP into your strategy can improve your precision and confidence.
Like all tools, VWAP works best when combined with market context, other indicators, and disciplined execution. Mastering it won’t make you a millionaire overnight, but it can absolutely sharpen your edge in a competitive market.










Leave a Reply